Schizophrenia is a complex brain disorder that profoundly affects how a person thinks, feels, and behaves, often challenging perceptions of reality. Understanding what happens in schizophrenia is not just about clinical definitions; it is about grasping the human experience behind the diagnosis and recognizing the immense potential for recovery and a fulfilling life with proper support. This comprehensive guide navigates the intricate world of schizophrenia, exploring its origins, the profound impact it has on the individual and their loved ones, and the innovative ways science and compassionate care are illuminating paths toward stability and well-being. We aim to demystify the condition, offering clarity on its symptoms, underlying neurological changes, and the range of effective treatments available, thereby empowering individuals to seek help, foster empathy, and combat the persistent stigma associated with mental illness. Discover why early intervention matters and how a supportive environment truly makes a difference in shaping positive outcomes for those living with this condition.
What truly happens in schizophrenia, and how does this complex condition alter a persons reality? This question sits at the heart of our exploration, as we delve into a brain disorder that affects millions globally, profoundly influencing how individuals perceive the world, process information, and interact with others. Who is typically affected by schizophrenia, and when does it usually emerge? This condition frequently manifests in young adulthood, typically between the late teens and early thirties, touching people from all walks of life, regardless of their background or geographic location. Why is understanding what happens in schizophrenia so critically important? Because clearer insight helps us to dismantle pervasive myths, reduce stigma, and champion more effective support systems, truly empowering those who navigate its challenges daily. Where can individuals and families find reliable information and compassionate care? Throughout this discussion, we will explore various avenues for support and treatment, showing how a comprehensive approach can significantly improve quality of life. How do these intricate brain changes unfold, and what can we do to foster better outcomes? Prepare to journey through the latest research and practical strategies designed to empower, educate, and offer hope for a brighter future.
Demystifying Schizophrenia: What Happens with Perception and Thought?
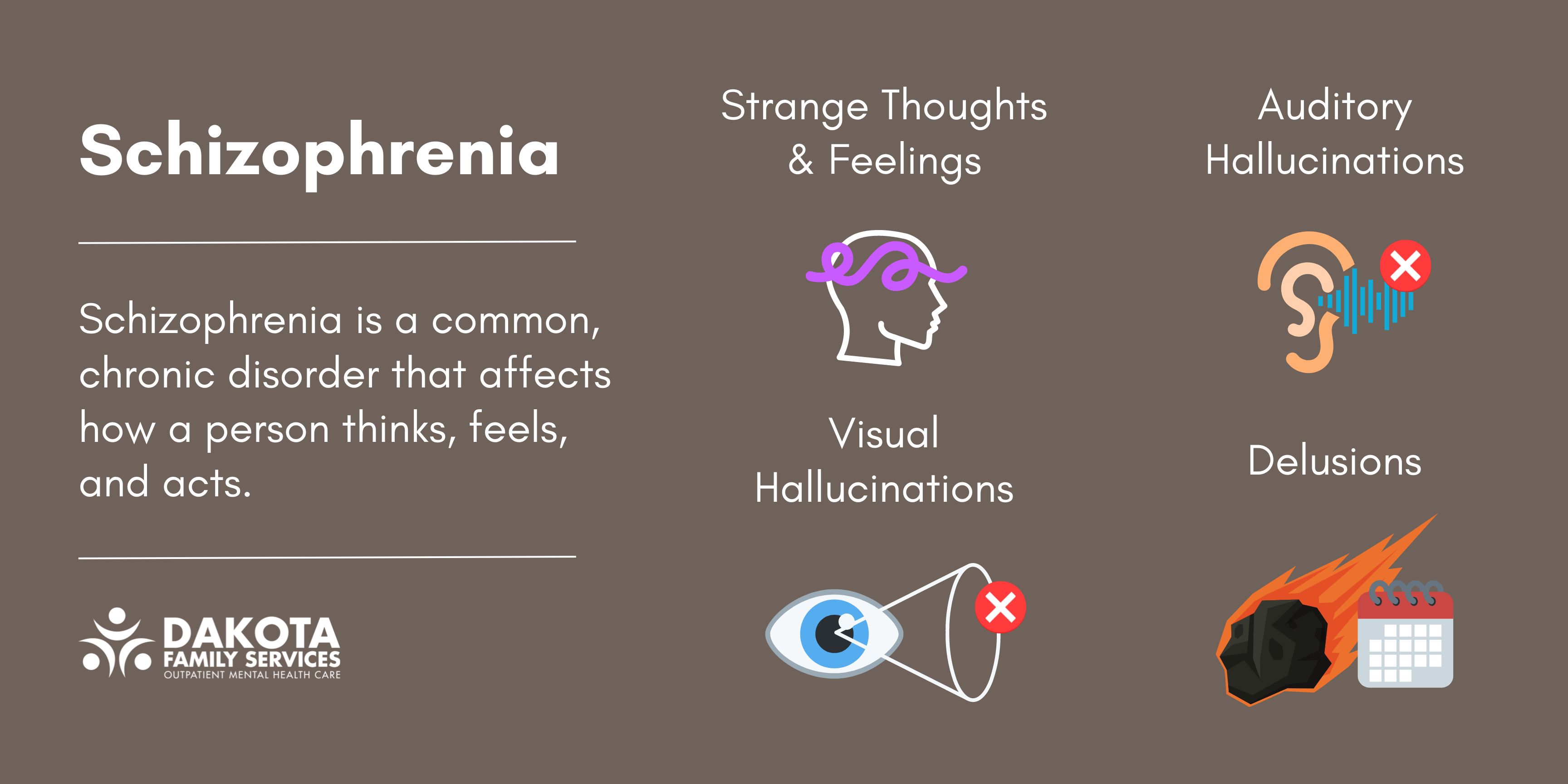
When someone experiences schizophrenia, what exactly unfolds in their mind to create such a profound shift in their perception of reality? This condition primarily involves a severe disruption in thought processes, emotional responses, and behavior, making it incredibly challenging for individuals to distinguish between what is real and what is not. What are the hallmark symptoms that characterize this experience, and how do they impact daily life? People often encounter positive symptoms, which are additions to normal experience, such as hallucinations where they see or hear things others don’t, and delusions, which are strong, false beliefs not based in reality. For instance, why would someone believe they are being persecuted or have special powers? These beliefs feel undeniably true to the person experiencing them, shaping their decisions and interactions. Additionally, disorganized thinking, often visible in jumbled speech or difficulty connecting thoughts logically, makes communication hard. How does this confusion affect their relationships and their ability to hold a job? The struggle is immense, highlighting the urgent need for understanding and support as we explore what happens in schizophrenia.
Beyond the more dramatic positive symptoms, what other aspects of what happens in schizophrenia contribute to its complexity and impact on a persons life? Many individuals also experience negative symptoms, which describe a reduction or absence of normal functions, rather than an addition. What does this mean in practical terms, and how do these symptoms manifest? These can include a lack of motivation or interest in activities, known as avolition, where even simple tasks become monumental challenges. Why might someone appear withdrawn or unable to express emotions? This emotional flatness, or reduced affect, can make it difficult for others to connect with them, even though the person might be feeling intensely inside. Furthermore, where does one find the energy or desire to pursue goals when apathy becomes a constant companion? Cognitive symptoms also play a significant role, affecting memory, attention, and executive functions like problem-solving and decision-making. How do these struggles with clear thinking affect a persons ability to learn new things or manage their finances? Understanding these varied facets helps paint a fuller picture of the inner world of someone living with schizophrenia, moving beyond mere labels to a deeper, more empathetic comprehension of their daily battle.
The Brain on Schizophrenia: What Changes Within?
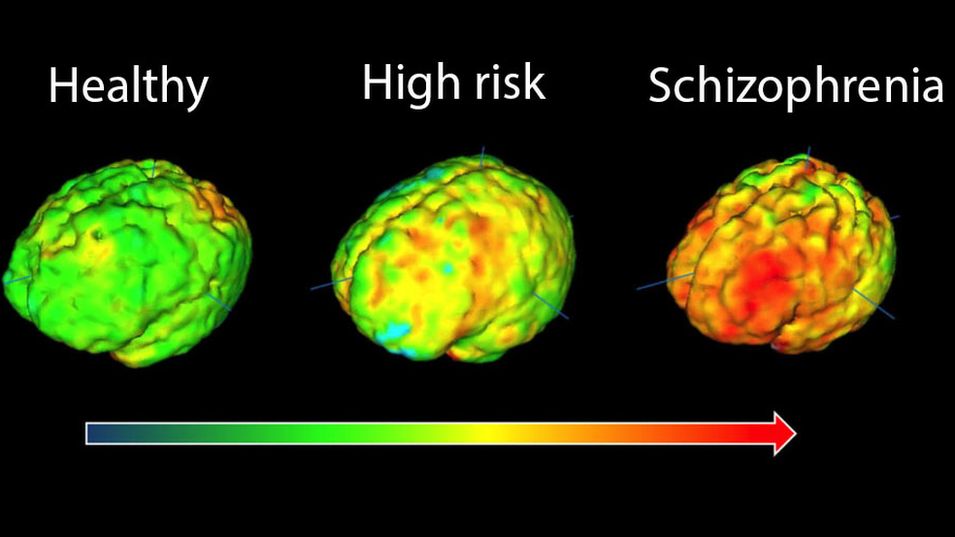
When we ask what happens in schizophrenia at a biological level, what does science tell us about the brain’s intricate workings? Research reveals that the brains of individuals with schizophrenia often show subtle yet significant differences in structure and function compared to those without the condition. What specific areas or systems are typically affected, and how do these changes contribute to the observed symptoms? Studies point to disruptions in neurotransmitter systems, particularly dopamine, which plays a crucial role in motivation, pleasure, and reward. Why might an imbalance in dopamine pathways lead to hallucinations and delusions, making someone perceive non-existent threats or hear voices? It is believed that an overactivity in certain dopamine pathways could contribute to these positive symptoms, while underactivity in others might explain the negative symptoms. Furthermore, where do these chemical imbalances originate, and are they the sole cause? The answer remains complex, involving a combination of genetic predispositions and environmental factors, all contributing to the unique presentation of what happens in schizophrenia for each individual.
Beyond neurotransmitter imbalances, what other structural or functional changes does the brain undergo when someone has schizophrenia? Neuroimaging studies have revealed subtle differences, such as slightly enlarged ventricles—fluid-filled spaces in the brain—and reductions in gray matter volume, especially in areas responsible for complex thinking and emotional regulation, like the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus. Why do these changes occur, and how do they influence a persons cognitive abilities and emotional responses? While these are often subtle and not universally present, they suggest a neurodevelopmental component, meaning that some changes might begin even before symptoms emerge. How does this impact the timing of symptom onset in young adulthood? It suggests a second hit or environmental trigger often interacts with a genetic vulnerability that has been subtly developing for years. Where does this leave us in terms of prevention or early intervention? Identifying these underlying brain changes helps us understand not just what happens in schizophrenia, but also how to develop more targeted and effective treatments that address these biological underpinnings, giving us hope for a future with better outcomes.
Spotting the Signs: How Does Schizophrenia Appear?
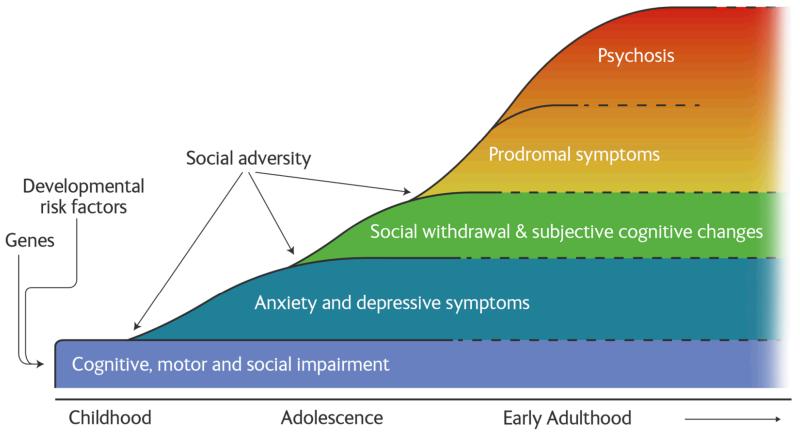
How does one recognize the earliest indicators of what happens in schizophrenia, especially when the onset can be gradual and insidious? Identifying the initial signs can be challenging, as the condition often begins with a prodromal phase where subtle changes in behavior, thoughts, and feelings emerge, often mimicking typical adolescent issues or other mental health conditions like depression or anxiety. What should family members and friends look for, and when is it appropriate to seek professional help? Early warning signs might include a noticeable decline in school or work performance, social withdrawal, unusual or eccentric behaviors, a new preoccupation with abstract or philosophical concepts, or a marked change in personal hygiene. Why would someone suddenly lose interest in hobbies they once loved or become increasingly suspicious of others without apparent reason? These shifts, especially when persistent and distinct from previous behavior, can be crucial cues. Where can concerned individuals turn for guidance during this often confusing period? Recognizing these subtle shifts and understanding what happens in schizophrenia can pave the way for timely intervention, making a significant difference in long-term prognosis.
Once more pronounced symptoms of what happens in schizophrenia appear, how do they disrupt a persons daily life and overall functioning? The impact can be profound, affecting every aspect from personal relationships to academic achievements and career paths. What are the common challenges individuals face when their perceptions of reality are altered by hallucinations or their thoughts become disorganized? Maintaining consistent employment often becomes difficult due to cognitive impairments or the overwhelming nature of their symptoms. Social interactions suffer as paranoia or withdrawal makes forming and maintaining connections arduous. Why do individuals sometimes struggle with self-care, like managing personal finances or keeping appointments? The cumulative effect of these challenges can lead to significant distress and isolation. How do families cope with these shifts, and where can they find resources to support their loved one and themselves? Understanding the breadth of these challenges is vital for developing comprehensive support systems that address not just the symptoms, but the full spectrum of a persons needs, fostering resilience and encouraging pathways to recovery.
| Aspect | Description of What Happens in Schizophrenia |
|---|---|
| Thought Processes | Experiences disorganized thinking, making logical conversation difficult; delusions (fixed, false beliefs) are common. |
| Perception | Often involves hallucinations, primarily auditory (hearing voices), but can also be visual, tactile, or olfactory. |
| Emotions | May show reduced emotional expression (flat affect) or emotions that do not match the situation. |
| Motivation | Reduced drive or interest in activities (avolition) and social withdrawal are frequent challenges. |
| Behavior | Can include unusual or repetitive movements, agitation, or a lack of self-care. |
| Onset | Typically emerges in late adolescence or early adulthood, affecting both men and women. |
| Causes | A complex interplay of genetic predisposition, brain chemistry imbalances (e.g., dopamine), and environmental factors. |
| Treatment | Involves antipsychotic medications, psychotherapy (CBT, family therapy), and comprehensive support services. |
Navigating Treatment: What Helps Most with Schizophrenia?
When an individual faces what happens in schizophrenia, what treatment avenues offer the most effective paths toward stability and improved quality of life? The cornerstone of treatment often involves antipsychotic medications, which help manage symptoms like hallucinations and delusions by balancing brain chemistry, particularly dopamine levels. How do these medications work, and why are they so crucial for symptom control? They primarily block dopamine receptors in specific brain areas, reducing overactivity and alleviating the positive symptoms that cause significant distress. However, medication is rarely a standalone solution. What other therapies complement pharmaceutical interventions, and how do they contribute to a more holistic recovery? Psychotherapy, such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), helps individuals develop coping strategies for persistent symptoms, challenge distorted thoughts, and learn practical skills for daily living. Why is a combination approach typically more effective than relying on one method? It addresses both the biological and psychological aspects of the condition, fostering resilience and personal growth.
Beyond medications and individual therapy, what additional supports and strategies prove invaluable in helping individuals navigate what happens in schizophrenia and thrive? Family therapy, for instance, plays a critical role by educating family members about the condition, improving communication patterns, and developing effective coping mechanisms as a unit. How does a supportive family environment impact an individuals recovery journey, and where can families find these resources? It reduces stress within the home, fosters understanding, and empowers loved ones to offer consistent, informed support, which is often a major predictor of positive outcomes. Furthermore, social skills training helps individuals regain confidence in social situations, practice appropriate interactions, and rebuild their social networks, addressing the isolation often experienced with the illness. Why is community integration so important for long-term well-being? Access to vocational training, supported employment programs, and peer support groups empowers individuals to achieve personal goals, contributing to a sense of purpose and belonging, and ultimately demonstrating that a fulfilling life is not only possible but achievable.
Empowerment and Hope: How to Live Well with Schizophrenia?
Facing the realities of what happens in schizophrenia can feel daunting, but how do individuals and their support networks cultivate empowerment and foster a life of purpose and well-being? It begins with accepting the diagnosis, understanding the illness, and committing to a consistent treatment plan. What are the practical steps someone can take to actively manage their symptoms and enhance their quality of life? Regular medication adherence, engaging in therapy, and developing robust coping strategies are fundamental. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle—including balanced nutrition, regular exercise, and sufficient sleep—also plays a significant role in overall mental and physical health. Why is self-advocacy so powerful for individuals living with this condition? Learning to voice needs, ask questions, and actively participate in treatment decisions gives a person agency, transforming them from a passive recipient of care into an active participant in their recovery journey. Where can one find resources for self-advocacy and peer support groups that offer shared experiences and mutual encouragement? These communities provide invaluable insights and a sense of belonging, showing that you are not alone on this path.
Beyond personal management, what larger societal efforts and attitudes significantly impact how someone lives with what happens in schizophrenia? Challenging stigma and promoting widespread mental health literacy are paramount. Why does societal stigma persist, and how does it create additional barriers for individuals seeking help or living openly with their diagnosis? Misconceptions and fear often lead to discrimination, social exclusion, and reluctance to seek necessary care, intensifying the burden of the illness. How can each of us contribute to dismantling these harmful stereotypes and fostering a more compassionate society? By educating ourselves, speaking openly about mental health, and supporting policies that advocate for equitable access to care, we collectively create environments where individuals feel safe, respected, and empowered to thrive. Where do we find stories of resilience and success that can inspire others? Countless individuals live full, meaningful lives with schizophrenia, managing their symptoms and contributing richly to their communities. Their stories are not just tales of survival but powerful testaments to human strength, reminding us that hope is not just a wish, but a tangible outcome for those who understand what happens in schizophrenia and actively pursue wellness.
Summary Question and Answer: What truly happens in schizophrenia? It involves complex brain changes affecting perception, thought, and emotion, often manageable with consistent support and treatment, empowering individuals to lead fulfilling lives.
Keywords: schizophrenia symptoms, schizophrenia causes, schizophrenia treatment, living with schizophrenia, understanding psychosis, mental health awareness, brain changes schizophrenia, early signs of schizophrenia, managing schizophrenia, mental illness facts.
Schizophrenia is a brain disorder impacting thought, emotion, and behavior. Symptoms include hallucinations, delusions, disorganized thinking, and reduced motivation. Brain chemistry and structure show differences, with genetics and environment playing roles. Early intervention and consistent treatment significantly improve outcomes. Treatment involves medication, psychotherapy, and community support. Understanding and empathy are crucial for reducing stigma and promoting recovery.
Early Signs Of In Kids Teens And Adults Early Signs 5101519 Final What Are The Different Types Of What Are The Symptoms Of 2953120 Mapping How Changes Brains Pursuit By The University Of Mapping How Changes Brains 1274a19c 834a 49b2 9772
What Age Does Start Age Of Onset 5194845 DD Final General Information Deadlines Research 2026 Banner 1024x277 Brain Scans Changes And Early Signs Brain 5193049 Final Causes Symptoms And Treatment Ausmed 20200204 Cover B V3
In Teens Symptoms Causes Type Treatment Types Of 1024x576 Infographic 681a865b 3bbf 4696 Ae30 Navigating Health Insights And Tips From Kailash Hospital S Blog In Teen What Happens In The Brain When People With Hear Voices AdobeStock 877818299 2048x1152
What Does To Families And Why The Mental Health System Imrs.phpHave You Got The Wrong Impression About BBC News 86138689 Brainscans What Is Infographic Video Approach To Spectrum And Other Psychotic Disorders
Young Adults With Face Highest Suicide Risk Study Says Ya Sucide 03 Does Get Worse With Age My Pic 2 800x400 Causes Risks Triggers Treatment Copy Of Symptoms Infographic 768x768 Unit 1 What Is The Definition Of KNILT Of
Spectrum Disorders And How To Manage Them Spectrum And Types 5193053 FINAL The Evolution Of Pursuit By The University Of Melbourne The Evolution Of 53efdb94 79f7 4a28 A44e An Integrated Cognitive Model PMC Emss 59737 F0001 Symptoms Mood And Behavior Effects Sign Symptoms 5095511 Final
What Is Youth Medical Journal O4 KDQkTVWhat Happens In The Brain When People With Hear Voices AdobeStock 501760386 1024x576 Awareness Day 2023 Removing The Stigma Around Mental Health 88a013 What It Is Causes Symptoms Treatment 4568
Symptoms Causes Type And Treatment What Is Foliotor Blog Identifying In Children 4155780 World Day Third Academy Research 748582
National Institute Of Mental Health NIMH 2022 Twitter Coping With How To Calm A Case Statistics For Patients In The USA 626x1024 What Is Myths Dakota Family Services Glossary Graphic

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/schizophrenia-spectrum-and-types-5193053-FINAL-ff64839e31a64ca293f12f168d488302.jpg)


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/schizophrenia-sign-symptoms-5095511_final-57a52853a10c4edcb4bd6a3b31f041ea.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/schizophrenia-age-of-onset-5194845-DD-Final-073c34baac324491b881053833777014.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/early-signs-schizophrenia-5101519_final-6861147c5e4e4a09956011952057ba72.jpg)










/identifying-schizophrenia-in-children-4155780-88bc55cd9a3247e1b794167e6a0d4667.png)
